
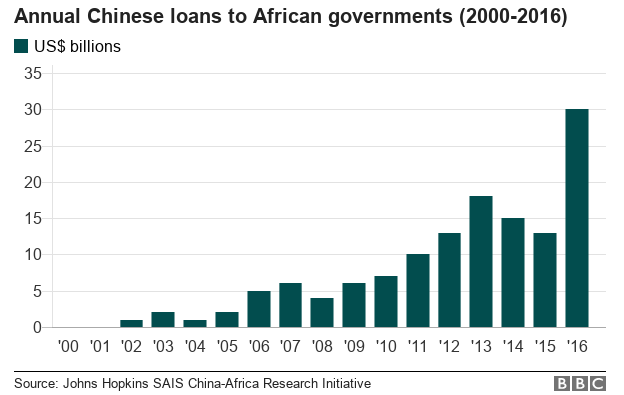
African countries have shown a healthy appetite for Chinese loans but some experts now worry that the continent is gorging on debt, and could soon choke.
The Entebbe-Kampala Expressway is still something of a tourist attraction for Ugandans, nearly three months after it opened.
The 51km (31 mile), four-lane highway that connects the country's capital to the Entebbe International Airport was built by a Chinese company using a $476m (£366m) loan from the China Exim Bank.
It has cut what was a torturous two-hour journey through some of Africa's worst traffic into a scenic 45-minute drive into the East Africa nation's capital.

The new expressway was financed with millions of dollars from China
Uganda has taken $3bn of Chinese loans as part of a wider trend that Kampala-based economist Ramathan Ggoobi calls its "unrivalled willingness to avail unconditional capital to Africa".
"This debt acquired from China comes with huge business for Chinese companies, particularly construction companies that have turned the whole of Africa into a construction site for rails, roads, electricity dams, stadia, commercial buildings and so on," the Makerere University Business School lecturer told the BBC.
The Chinese loans come as many African countries are once again in danger of defaulting on their debts more than a decade after many had their outstanding borrowing written off.
At least 40% of low-income countries in the region are either in debt distress or at high risk, the International Monetary Fund warned in April.
Chad, Eritrea, Mozambique, Congo Republic, South Sudan and Zimbabwe were considered to be in debt distress at the end of 2017 while Zambia and Ethiopia were downgraded to "high risk of debt distress".
"In 2017 alone, the newly signed value of Chinese contracted projects in Africa registered $76.5bn," Standard Bank's China Economist Jeremy Stevens wrote in a note.
"However, despite a sizeable remaining infrastructure deficit on the continent, there is a concern that African countries' debt-service ability will soon dissolve," he says.
The Chinese model has many high-profile defenders on the continent, including the head of the African Development Bank (ADB) Akinwumi Adesina, a former Nigerian agriculture minister.
"A lot of people get nervous about China but I am not. I think China is Africa's friend," he told the BBC.
China is now the single largest bilateral financier of infrastructure in Africa, surpassing the ADB, the European Commission, the European Investment Bank, the International Finance Corporation, the World Bank and the Group of eight (G8) countries combined.
The money's impact is conspicuous all over Africa, from shiny new airports and roads as well as ports and high-rise buildings that are also creating much-needed jobs.
In fact, a McKinsey and Company analysis found that the amount of loans Beijing had made to Africa had tripled since 2012, including an outsize $19bn to Angola alone in 2015 and 2016.
It cited Angola and Zambia as unbalanced partners with China in Africa.

China's investment in Zambia has been controversial
"In Angola's case, the government has supplied oil to China in exchange for Chinese financing and construction of major infrastructure projects - but market driven private investment by Chinese firms has been limited compared with other African countries," the firm said.
Africa has made significant new gains in trade, investment and financing arrangements with China, says Ghanaian investment analyst Michael Kottoh.
"There are several truly win-win deals African nations have closed without the typical onerous conditions associated historically with doing business with western countries," says Mr Kottoh, whose advisory firm Konfidants counsels international clients.
"But there is a sense in which China is obviously the bigger winner - simply because it has the upper leverage in most negotiations."
McKinsey projects that revenues for Chinese firms in Africa could hit $440bn by 2025.
Even Mr Adesina agreed that: "The issue that I have seen is the asymmetry of power in the negotiations of the transactions, where you are actually giving your mining rights away just because you want to build a superhighway.
"You are only dealing with one country, how are you sure that you are getting the best deal?"
China does not have a Foreign Corrupt Practices Act like the United States, or similar legislation in other Western countries that criminalise bribes paid overseas in exchange for contracts.
Even though Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz calls the Western criticism of China's work in Africa "sour grapes," he admits that there are corruption concerns.
"Every project whether it comes from the west or China needs to be evaluated against the rate of returns," he told the BBC in Nairobi but added that it was up to the continent's governments to be more transparent.
Mr Ggoobi also says there are greater concerns over the environmental effects of Chinese investments, "particularly given the poor, weak, corrupt regulatory institutional infrastructure in Africa".
In 2015, the China Africa Research Initiative at the Johns Hopkins School of Advanced International Studies sounded alarm bells that African countries might be unable to repay Chinese loans "due to fluctuating commodity prices and decreasing absorptive capacity".
"We find that Chinese loans are not currently a major contributor to debt distress in Africa," they now say in a new briefing paper ahead of the 7th Forum on China Africa Cooperation Summit this week in Beijing.
China has the lion's share of African debt but the countries are borrowing from many other sources internationally so it is not single-handedly to blame for indebtedness.
When the summit last met, in Johannesburg, China promised $35bn in concessional foreign aid loans among other credit lines to Africa.
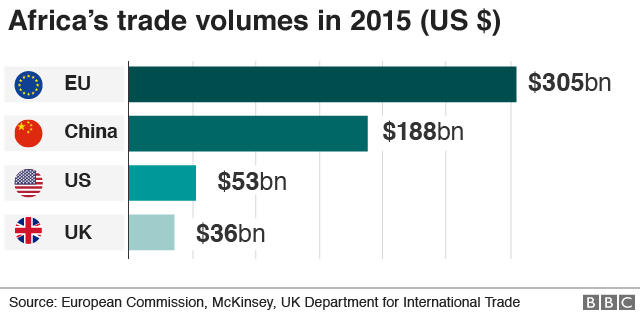
What has not improved is what Standard Bank calls a "significant trade deficit with China" since 2014. It says only five African countries have a trade surplus with China.
Mr Ggoobi wants China to help Africa build institutional capacity to attract and host viable investments using avenues like special economic zones and industrial parks to shore up the continent's export-focused manufacturing.

African leaders meet annually in the Chinese funded $200m headquarters in Ethiopia
So far, China has only paid lip service to such long-term support that would wean African countries off their dependency on the Asian tiger.
Djibouti last month launched the first phase of the Chinese-built free trade zone billed as Africa's largest but it is seen as just another piece of the jigsaw puzzle as China revives old trade routes in its Belt and Road Initiative which targets 60 countries.
Ugandans might enjoy soaring above the swampy Nambigirwa Bridge on their new expressway, but there are real fears that they could end up drowning in Chinese debt.