
Opposition to Amazon's sale of its facial recognition technology to US police forces is set to come to a head at its annual general meeting on Wednesday.
Shareholders will vote twice on the matter.
First, over whether the company should stop offering its Rekognition system to government agencies.
And second, over whether to commission an independent study into whether the tech threatens people's civil rights.
The votes are non-binding, meaning executives do not have to take specific action whatever the outcome.
Amazon had tried to block the votes but was told by the Securities and Exchange Commission that it did not have the right to do so.

Rekognition gives a confidence score as to whether a person's face is a match
"We're hopeful that we'll get strong support from other investors and that will send a signal to the company that they shouldn't move forward with sales to governments until or unless they are able to mitigate the risks," Mary Beth Gallagher from the Tri-State Coalition for Responsible Investment told the BBC.
"It could enable massive surveillance, even if the technology was 100% accurate, which, of course, it's not.
"We don't want it used by law enforcement because of the impact that will have on society - it might limit people's willingness to go in public spaces where they think they might be tracked."
Amazon has urged its shareholders to vote against the proposals saying it had not received a single report of the system being used in a harmful manner.
"[Rekognition is] a powerful tool... for law enforcement and government agencies to catch criminals, prevent crime, and find missing people," its AGM notes state.
"New technology should not be banned or condemned because of its potential misuse."

Amazon has promoted its tech as a tool to fight crime
Rekognition is an online tool that works with both video and still images and allows users to match faces to pre-scanned subjects in a database containing up to 20 million people provided by the client.
In doing so, it gives a confidence score as to whether the ID is accurate.
In addition, it can be used to:
Amazon recommends that law enforcement agents should only use the facility if there is a 99% or higher confidence rating of a match and says they should be transparent about its usage.
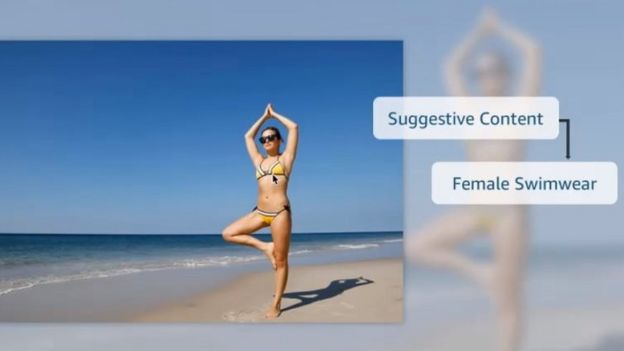
Rekognition can be used to flag "suggestive content"
But one force that has used the tech - Washington County Sheriff's Office in Hillsboro, Oregon, - told the Washington Post that it had done so without enforcing a minimum confidence threshold, and had run black-and-white police sketches through the system in addition to photos.
A second force in Orlando, Florida has also tested the system. But Amazon has not disclosed how many other public authorities have done so.
Part of Rekognition's appeal is that it is cheaper to use than several rival facial recognition technologies.
But a study published in January by researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the University of Toronto suggested Amazon's algorithms suffered greater gender and racial bias than four competing products.
It said that Rekognition had a 0% error rate at classifying lighter-skinned males as such within a test, but a 31.4% error rate at categorising darker-skinned females.

Amazon said that it ran tests against images of men and women from six ethnicities to check for signs of bias
Amazon has disputed the findings saying that the researchers had used "an outdated version" of its tool and that its own checks had found "no difference" in gender-classification across ethnicities.
Even so, opposition to Rekognition has also been voiced by civil liberties groups and hundreds of Amazon's own workers.
Ms Gallagher said that shareholders were concerned that continued sales of Rekognition to the police risked damaging Amazon's status as "one of the most trusted institutions in the United States".
But one of the directors from Amazon Web Services - the division responsible - said that it should be up to politicians to decide if restrictions should be put in place.

Rekognition can give a confidence score for several different features
"The right organisations to handle the issue are policymakers in government," Ian Massingham told the BBC.
"The one thing I would say about deep learning technology generally is that much of the technology is based on publicly available academic research, so you can't really put the genie back in the bottle.
"Once the research is published, it's kind of hard to 'uninvent' something.
"So, our focus is on making sure the right governance and legislative controls are in place."