
The death toll from the coronavirus outbreak has risen to 170, and a confirmed case in Tibet means it has reached every region in mainland China.
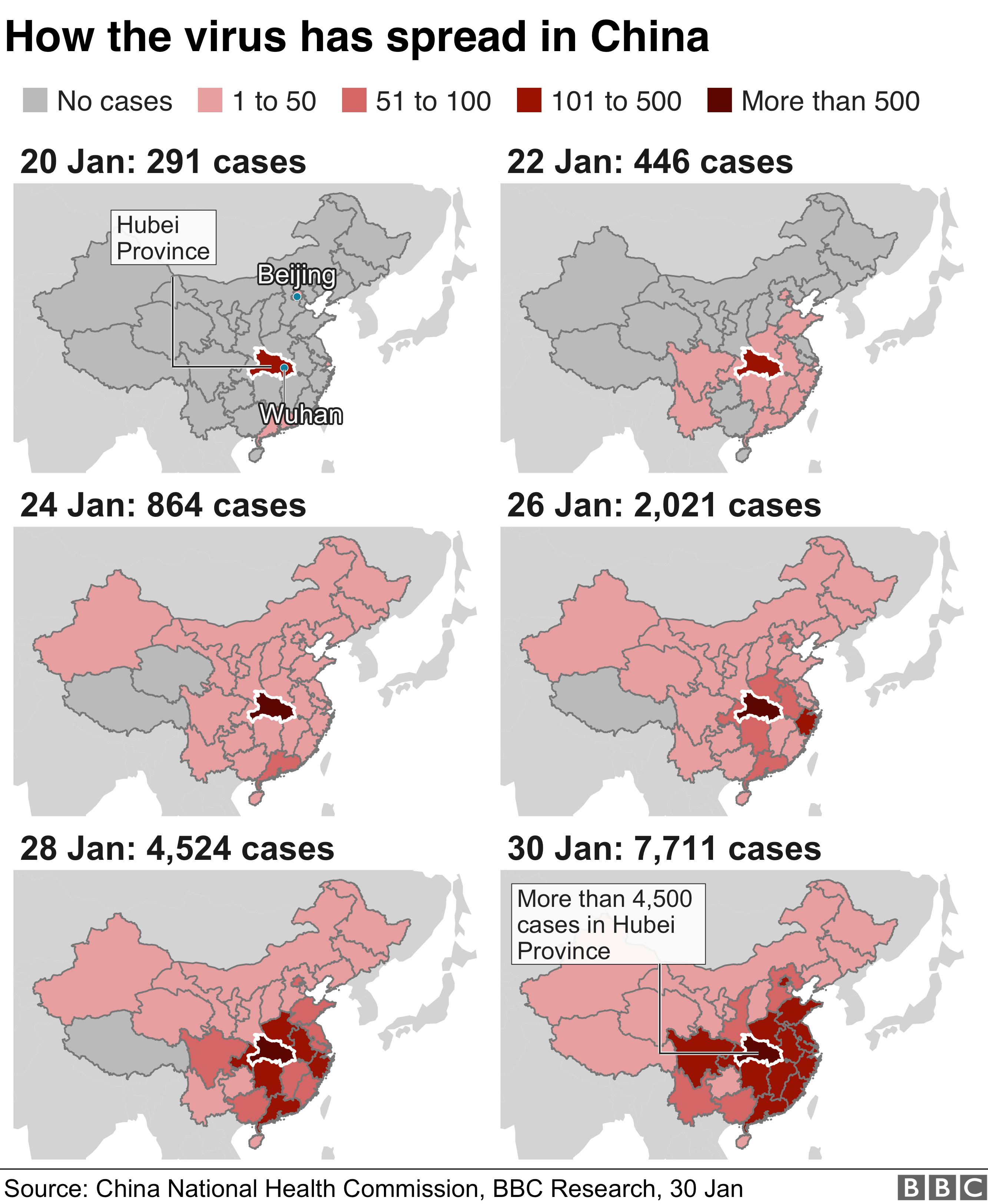
Chinese health authorities said there were 7,711 confirmed cases in the country as of 29 January.
Infections have also spread to at least 15 other countries.
The World Health Organization (WHO) will meet on Thursday to again consider whether the virus constitutes a global health emergency.
"In the last few days the progress of the virus, especially in some countries, especially human-to-human transmission, worries us," WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said on Wednesday.
He named Germany, Vietnam and Japan, where there have been cases of people catching the virus from others who have been to China.
"Although the numbers outside China are still relatively small, they hold the potential for a much larger outbreak," the WHO chief said.
More people have now been infected in China than during the Sars outbreak in the early 2000s, but the death toll remains far lower. Sars, also a coronavirus, caused acute respiratory illness.
Researchers are racing to develop a vaccine to protect people from the virus. One lab in California has plans for a potential vaccine to enter human trials by June or July.
Voluntary evacuations of hundreds of foreign nationals from Wuhan are under way to help people who want to leave the closed-off city and return to their countries.
The UK, Australia, South Korea, Singapore and New Zealand are expected to quarantine all evacuees for two weeks to monitor them for symptoms and avoid any contagion.
Australia plans to quarantine its evacuees on Christmas Island, 2,000km (1,200 miles) from the mainland in a detention centre that has been used to house asylum seekers.
Singapore is setting up a quarantine facility on Pulau Ubin, an island north-east of the city-state's mainland.
In other developments:
How is China handling the outbreak?
Although questions have been raised about transparency, the WHO has praised China's handling of the outbreak. President Xi Jinping has vowed to defeat what he called a "devil" virus.
The central province of Hubei, where nearly all deaths have occurred, is in a state of lockdown. The province of 60 million people is home to Wuhan, the heart of the outbreak.
The city has effectively been sealed off and China has put numerous transport restrictions in place to curb the spread of the virus.

The WHO warns the virus holds the potential for a much larger outbreak
People who have been in Hubei are also being told by their employers to work from home until it is considered safe for them to return.
The virus is affecting China's economy, the world's second-largest, with a growing number of countries advising their citizens to avoid all non-essential travel to the country.
Several international airlines have stopped or scaled back their routes to China and companies like Google, Ikea, Starbucks and Tesla have closed their shops or stopped operations.
There have been reports of food shortages in some places. State media says authorities are "stepping up efforts to ensure continuous supply and stable prices".
The Chinese Football Association has announced the postponement of all games in the 2020 season.
Although there have been nearly 8,000 infections, there has been little detailed information released on the profiles of patients and how the disease affects them.
Most of the confirmed cases involve people either from Wuhan or who had close contact with someone who had been there.
A new study published by The Lancet medical journal gives a snapshot of 99 cases of the new coronavirus observed at Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital from 1-20 January. It reveals: